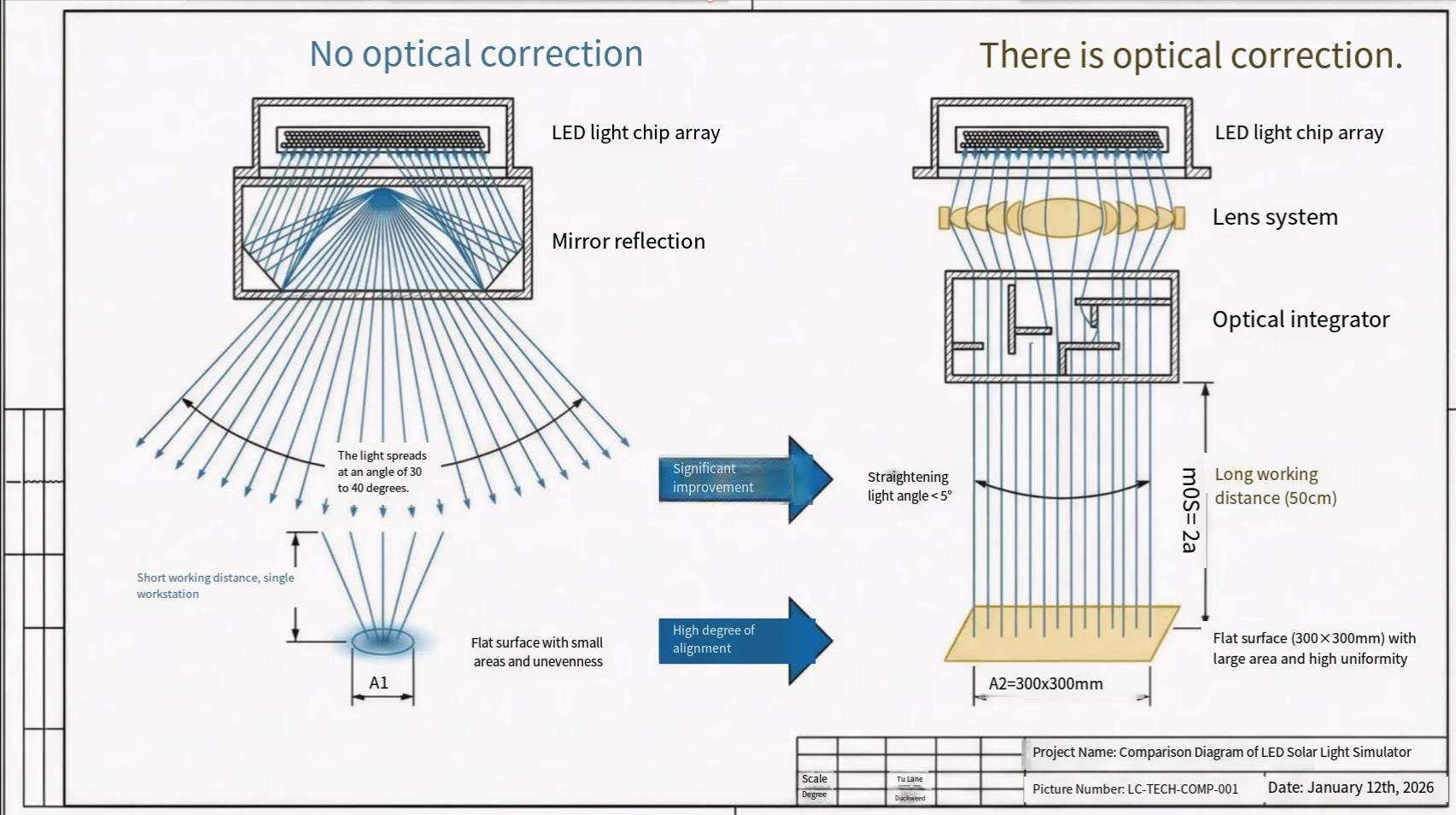
Thin-Film Solar Breakthroughs: Paving the Way for a Flexible and Efficient Energy Future
Keywords: Thin-Film Solar Materials, Perovskite Solar Cells, CZTS, Laser Annealing, Industrialization
A series of recent breakthroughs in thin-film photovoltaic materials are signaling a significant step toward more efficient, stable, and cost-effective solar energy solutions. From innovative manufacturing techniques to record-setting efficiencies, these advancements are expanding the potential of solar technology beyond rigid panels to flexible, lightweight applications integrated into buildings, vehicles, and even wearable devices.

Pushing the Efficiency Frontier
The quest for higher efficiency continues to yield impressive results. A research team from the Chinese Academy of Sciences recently announced the development of a perovskite solar cell with a certified photoelectric conversion efficiency of 27.2%, a remarkable figure for the technology
. Crucially, this device also addressed perovskite's historical Achilles' heel—stability. It maintained 86.3% of its initial efficiency after operating for over 1500 hours under continuous light, a key milestone for commercial viability .
Simultaneously, research on materials that are more abundant and less toxic than traditional options is progressing. A team from Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications has made strides with copper-zinc-tin-sulfur-selenide (CZTS) films. By refining the solution-based fabrication process, they successfully created a high-quality photovoltaic film with an area of 10.48 cm², achieving an efficiency of 10.1%. This validates a path toward inexpensive, environmentally friendly, and scalable thin-film solar cells .

Revolutionizing Manufacturing for Mass Production
A major hurdle for perovskite solar cells has been the sensitivity of the materials to ambient air during manufacturing, which typically requires energy-intensive, inert-gas environments. A groundbreaking solution comes from Nanchang University, where researchers developed a novel "laser annealing" technique.
This method, which crystallizes the perovskite film in just 20 seconds using a high-power blue laser, can be performed in open air. It bypasses the need for controlled atmospheres and represents a significant leap toward high-throughput, low-energy, and low-cost industrial production.
Market Trajectory and Future Outlook
These technological innovations are set against a backdrop of strong market growth. The global thin-film photovoltaics market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12-15% from 2025 to 2035, potentially increasing its market share from 5-7% to 10-12%. This growth is largely driven by the unique advantages of thin films, such as flexibility, light weight, and the emergence of building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) .
While challenges around long-term stability and material scarcity for some technologies persist, the recent convergence of efficiency gains, stability improvements, and innovative manufacturing processes marks a turning point. The transition of thin-film solar from a niche technology to a mainstream, competitive energy source appears closer than ever, promising a more versatile and sustainable energy future.