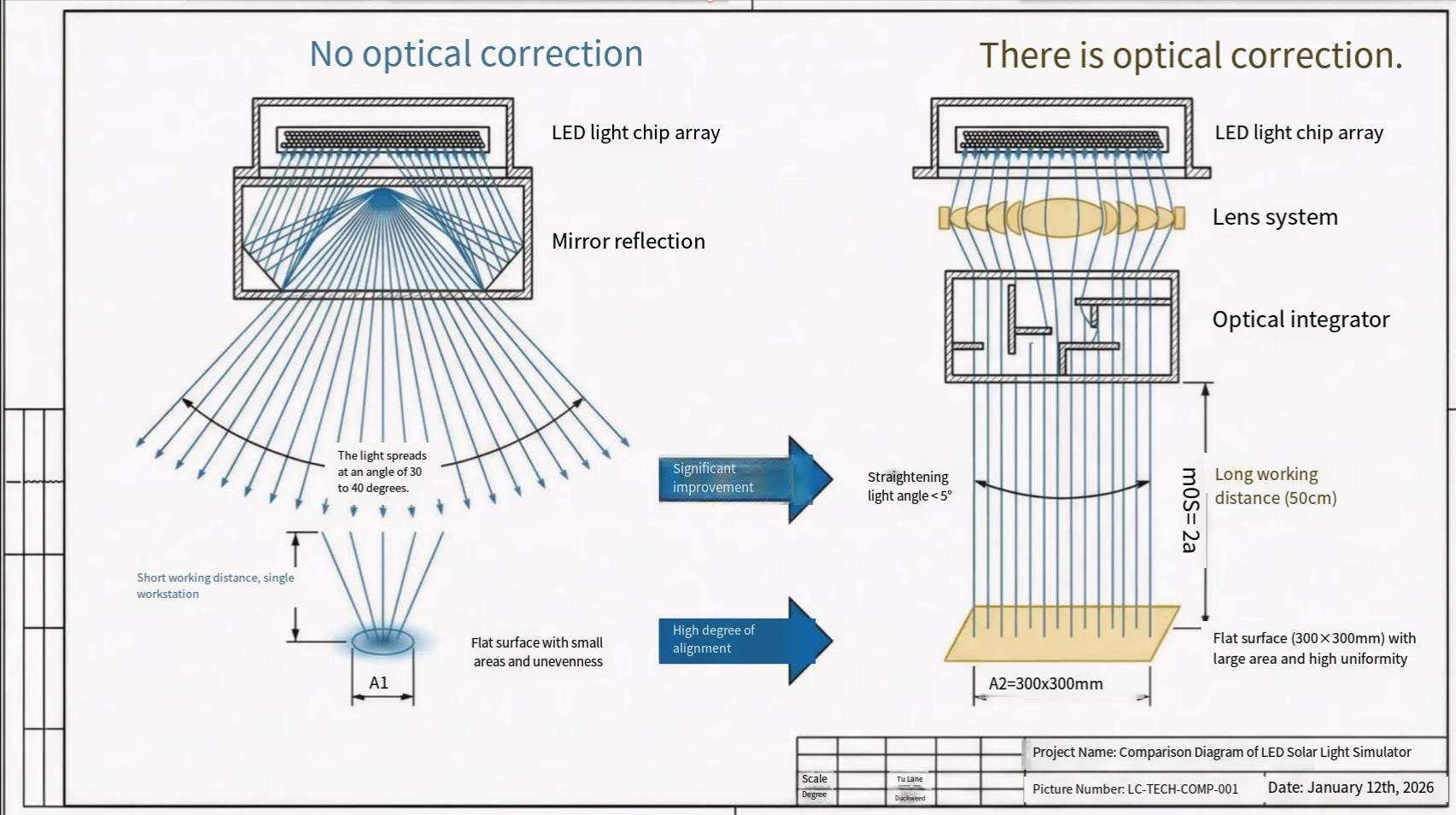
Introduction
The transition to gigawatt-scale perovskite solar production hinges on precision laser processing, where beam splitting technology plays a pivotal role. By dividing a single laser source into multiple beams, this technique enables simultaneous scribing of P1-P3 patterns and edge isolation (P4), directly impacting throughput, dead zone control, and production costs. Current industrial approaches primarily include mechanical beam splitting and diffractive optical elements (DOEs), each with distinct advantages for perovskite’s thermal sensitivity and scalability requirements.
Mechanical Beam Splitting: Stability for Large-Area Processing
Mechanical beam splitting employs precisely aligned mirrors and optics to partition a laser into synchronized sub-beams. German equipment leader LPKF utilizes this method in systems like the Allegro BK24, generating 12–24 beams with ±10 μm accuracy. The technology’s robustness stems from minimal power loss and resistance to thermal drift, critical for maintaining consistent ablation depth across meter-sized substrates (e.g., 1.2 m × 2.4 m panels). LPKF reports >98% uptime in GW-scale fabs, as mechanical systems avoid DOE-related alignment fragility
. Chinese manufacturer Lecheng Intelligent also adopts 12-path mechanical splitting, emphasizing real-time focus tracking to maintain kerf uniformity at speeds of 2 m/s .
DOE-Based Splitting: Scalability and Flexibility
DOE systems use micro-gratings to split beams, enabling higher multiplexing (e.g., 36 paths) at lower hardware costs. This suits high-mix production where laser parameters (wavelength, pulse duration) require frequent adjustments. However, DOEs incur 15–20% power loss and demand stringent calibration to prevent divergence in perovskite’s moisture-sensitive layers. Recent advances integrate adaptive optics to compensate for substrate deformation post-annealing, a common issue necessitating real-time trajectory tracking.
Performance Metrics: Throughput vs. Precision
Mechanical splitting excels in stability, achieving dead zones ≤130 μm via synchronous motion control—where glass substrates remain stationary while laser heads move, reducing vibration-induced errors. In contrast, DOE-driven systems prioritize speed: 36-beam configurations achieve scribing rates of 2,500 mm/s, but require post-process dead zone monitoring to avoid P1-P3 misalignment from material shrinkage
. For GW production, mechanical systems reduce the number of machines needed by 75% compared to standard 8-beam setups, slashing footprint and energy use .
Future Directions: Hybrid Systems and AI Optimization
Next-generation solutions aim to hybridize both technologies: mechanical splitting for P1/P3 baseline patterning, with DOE-modulated beams for dynamic P4 edge cleaning. AI-driven vision systems are being deployed to track line spacing in real-time, auto-adjusting beam positions to hold tolerances under ±5 μm. As Lecheng’s GW-scale prototypes indicate, adaptive beam splitting will be key to achieving <100 μm dead zones while supporting throughput exceeding 500 MW per machine.
Conclusion
Beam splitting technology is a critical enabler for perovskite photovoltaic industrialization, balancing speed and precision. While mechanical splitting offers reliability for foundational patterning, DOE-based methods provide scalability. The evolution toward intelligent, hybrid systems will ultimately determine the cost and efficiency benchmarks of next-generation solar manufacturing.