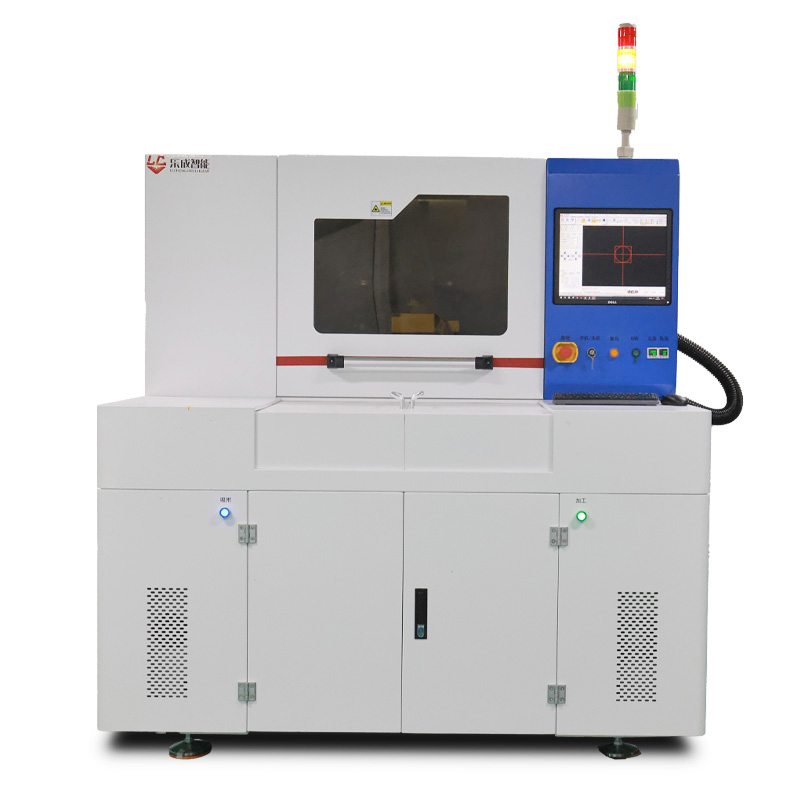
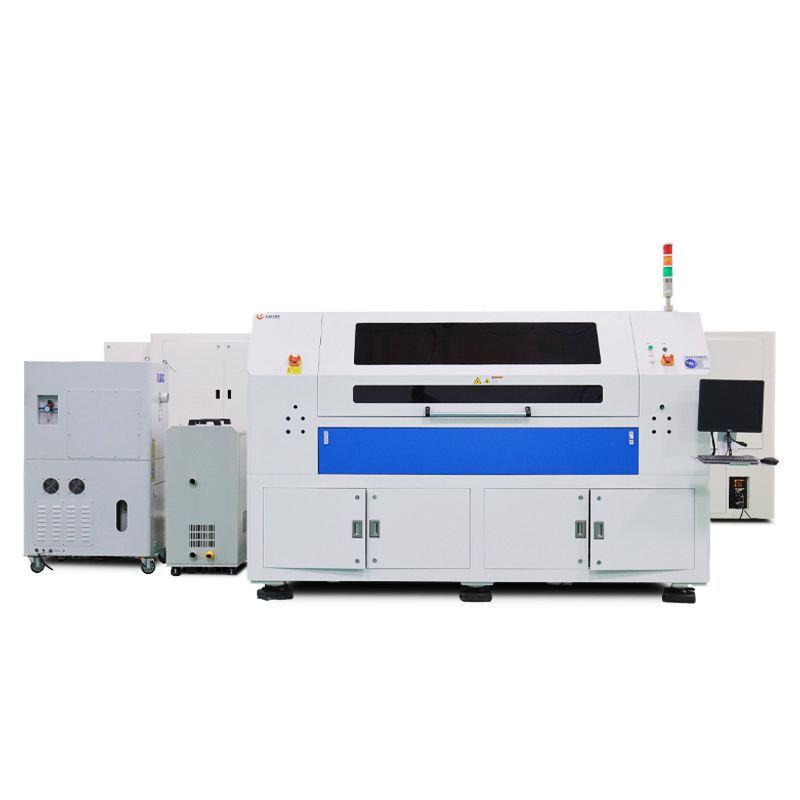
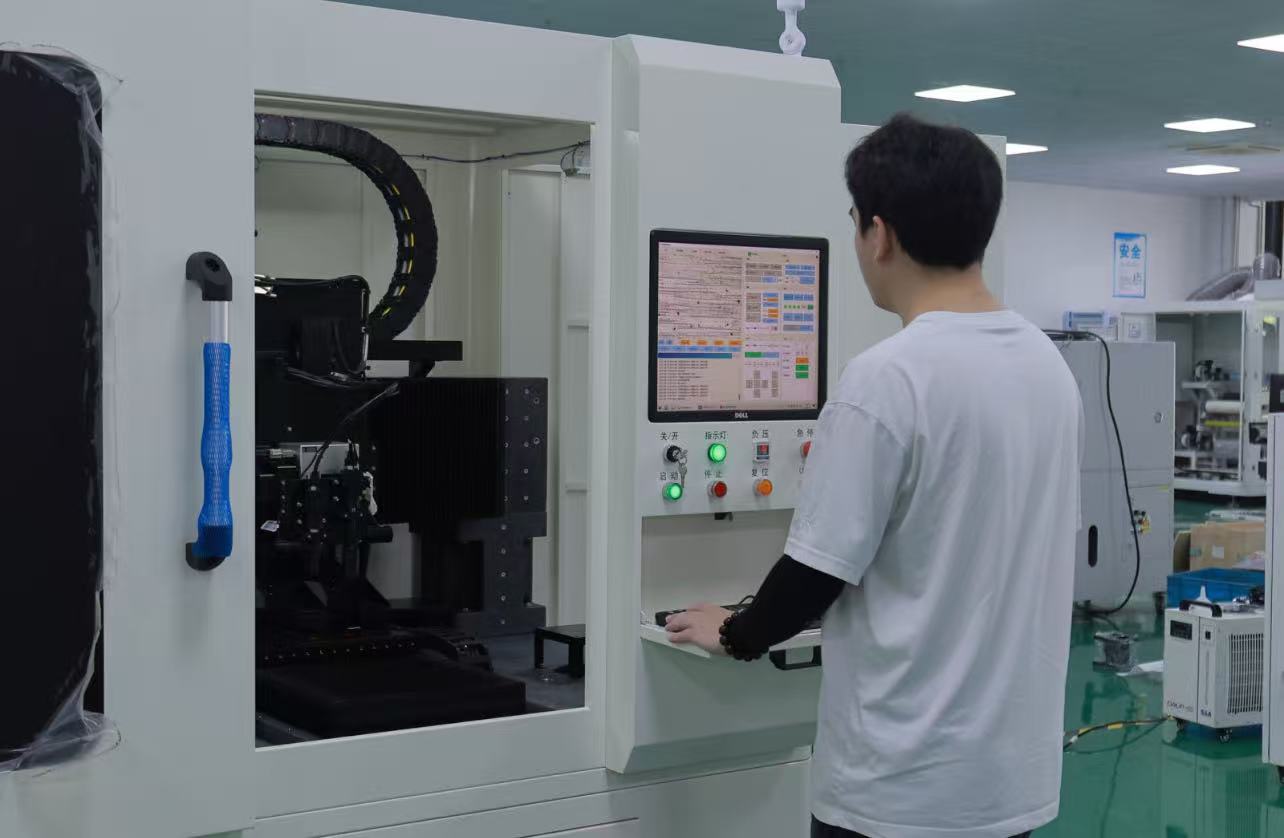
Lecheng’s Laser Edge-Cleaning System Solves Perovskite Edge Insulation Issues, Boosting Yield to 98%
1. The Critical Challenge of Edge Insulation in Perovskite Solar Modules
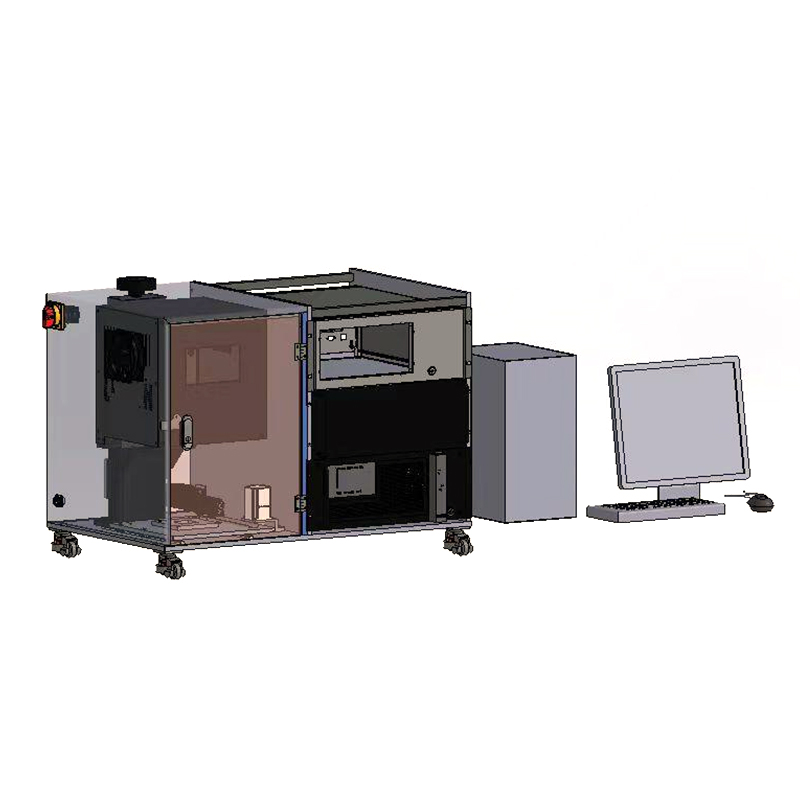
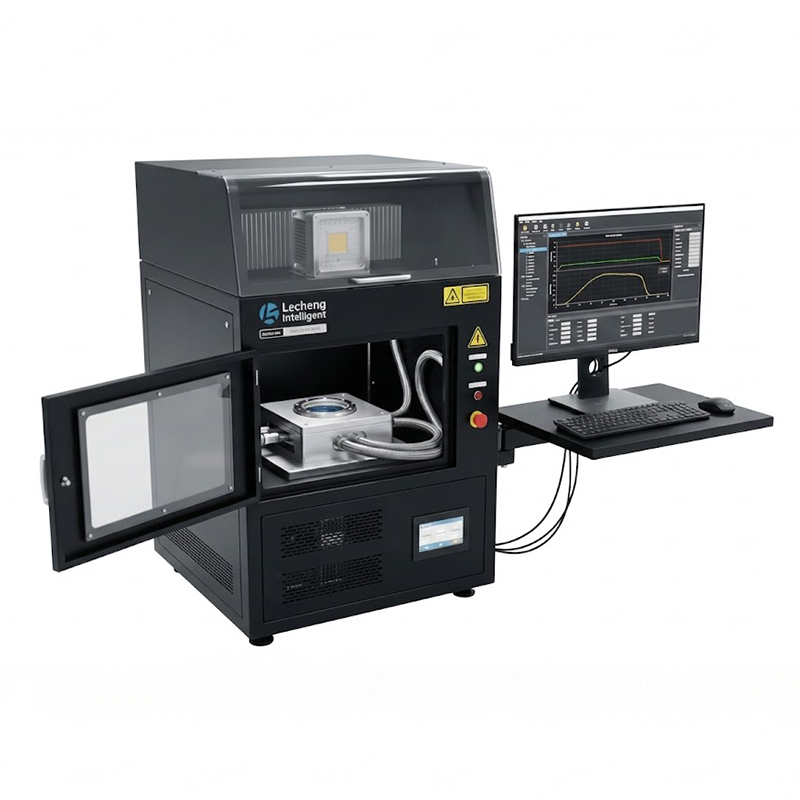
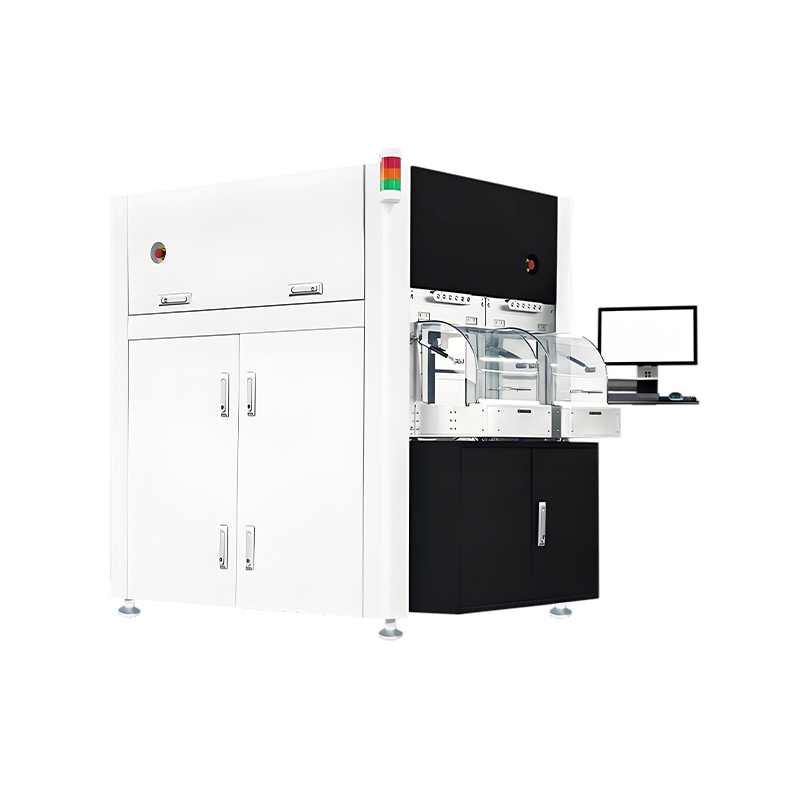
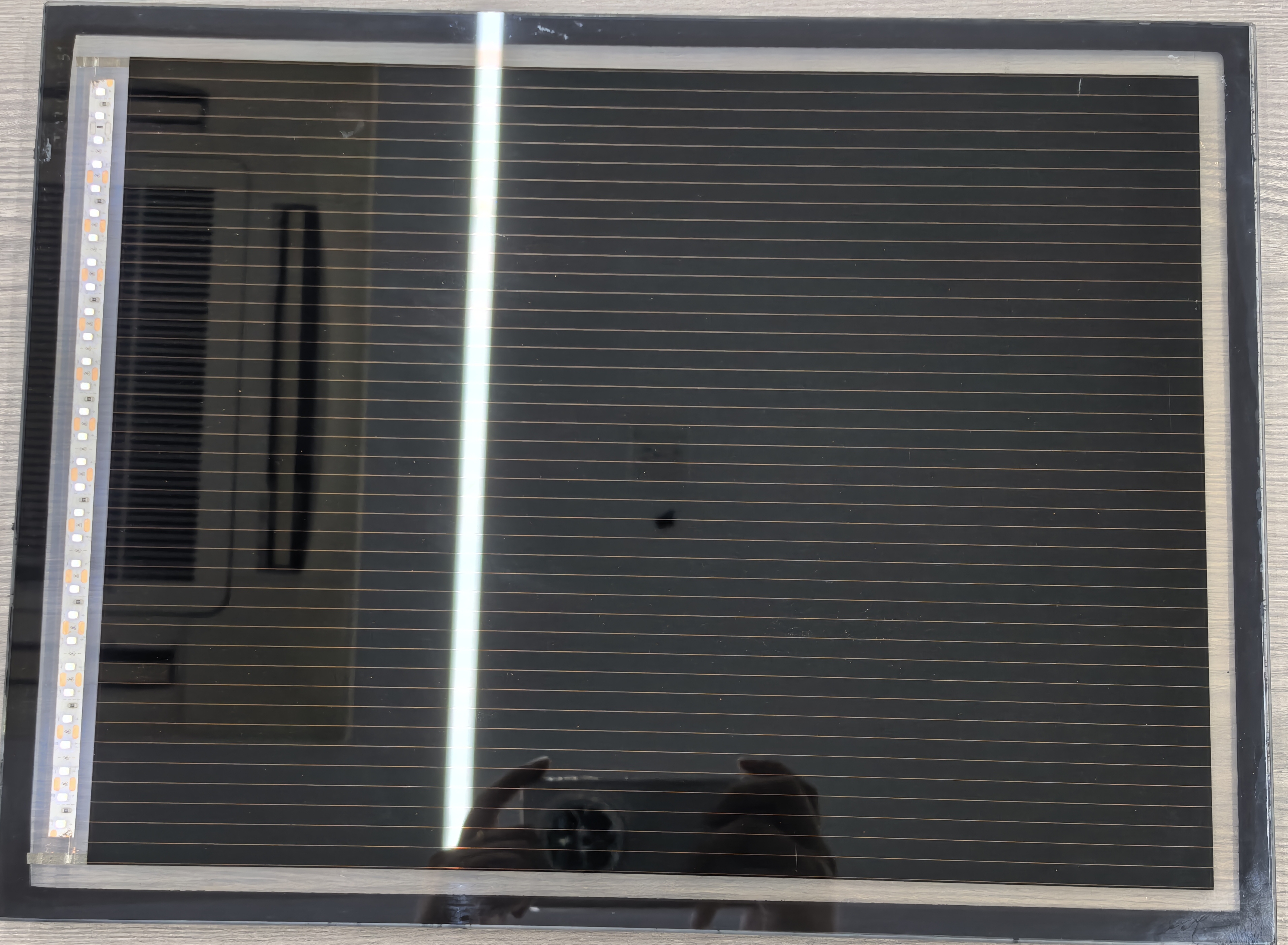
In perovskite solar manufacturing, edge insulation—known as the P4 process—is a decisive factor in module performance and longevity. During the deposition of multiple thin-film layers (TCO, HTL, perovskite, ETL, and back electrode), material overspray and interdiffusion at panel edges create micro-short circuits that leak current and cause rapid efficiency degradation. Traditional mechanical or chemical cleaning methods struggle to remove these complex multi-layer residues completely without damaging the active area or leaving contaminants. Lecheng Intelligent’s laser edge-cleaning system addresses this by using high-speed galvanometer scanners and optimized laser parameters to ablate edge deposits with micron-level precision. The system achieves a cleaning width accuracy of ±0.1mm, ensuring complete insulation while preserving the integrity of the functional layers. For large-format panels up to 2.4×1.2m, this process eliminates edge-induced current leakage, increasing module efficiency by 3–5% and enabling yield rates of 98%—a benchmark rarely achieved with conventional methods.
2. How Lecheng’s Laser Edge-Cleaning Technology Works
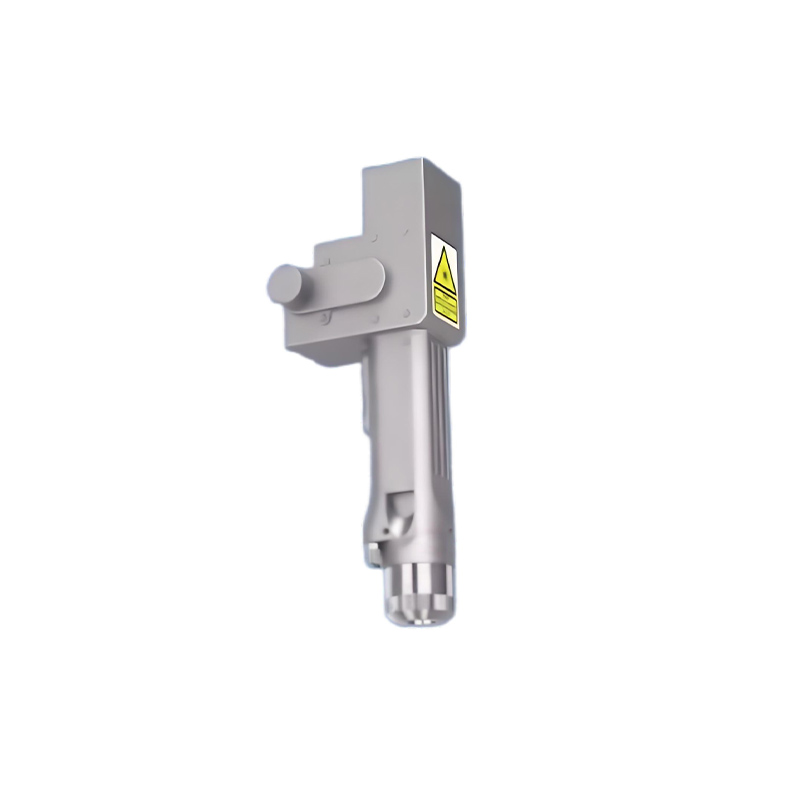
Lecheng’s system integrates three innovations to achieve unprecedented edge-cleaning quality. First, a multi-sensor alignment system combining CCD cameras and infrared sensors precisely locates panel edges and layer boundaries, adapting to positional variations up to ±2mm. Second, a proprietary laser source (fiber nanosecond lasers at 1064nm) delivers pulses with controlled energy density to vaporize residues without thermal damage to adjacent layers—critical for temperature-sensitive perovskite materials. The system’s “flying processing” mode allows continuous cleaning at speeds of 1.5m/min, synchronizing with the production line’s conveyor system. Third, real-time monitoring via integrated high-definition cameras detects defects such as incomplete ablation or layer damage, triggering automatic corrections or halting the process if deviations exceed tolerances. In mass production environments, this closed-loop control reduces manual intervention by 90% and cuts process time per panel by 40% compared to manual cleaning methods.

3. Impact on Perovskite Solar Manufacturing and Industry Adoption
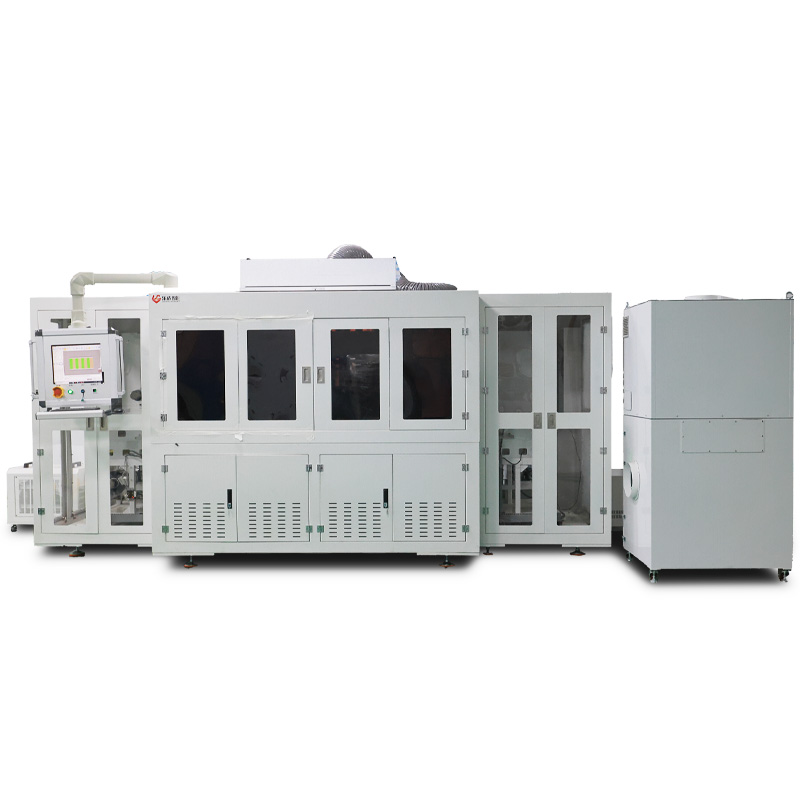
The reliability of Lecheng’s edge-cleaning system has made it a cornerstone in perovskite pilot lines and gigawatt-scale factories. For example, in a 100MW production line, the system consistently maintains insulation resistance above 100MΩ per module—exceeding industry standards—while enabling >98% yield across 10,000+ panels. Manufacturers also benefit from the system’s flexibility: it adapts to both rigid glass and flexible substrates, supports custom cleaning patterns (e.g., rounded corners or irregular shapes), and integrates with MES for data traceability. As perovskite technology evolves toward tandem cells and transparent modules, Lecheng’s technology continues to advance, with recent upgrades enabling cleaning widths as narrow as 0.5mm for high-density designs. By solving a critical bottleneck in perovskite manufacturing, Lecheng not only boosts productivity but also accelerates the commercialization of next-generation solar technologies.
Conclusion
Lecheng’s laser edge-cleaning system exemplifies how precision manufacturing technologies can transform solar energy economics. By ensuring flawless insulation at microscopic scales, it unlocks higher efficiency, reliability, and yield—bringing perovskite solar power closer to mainstream adoption.