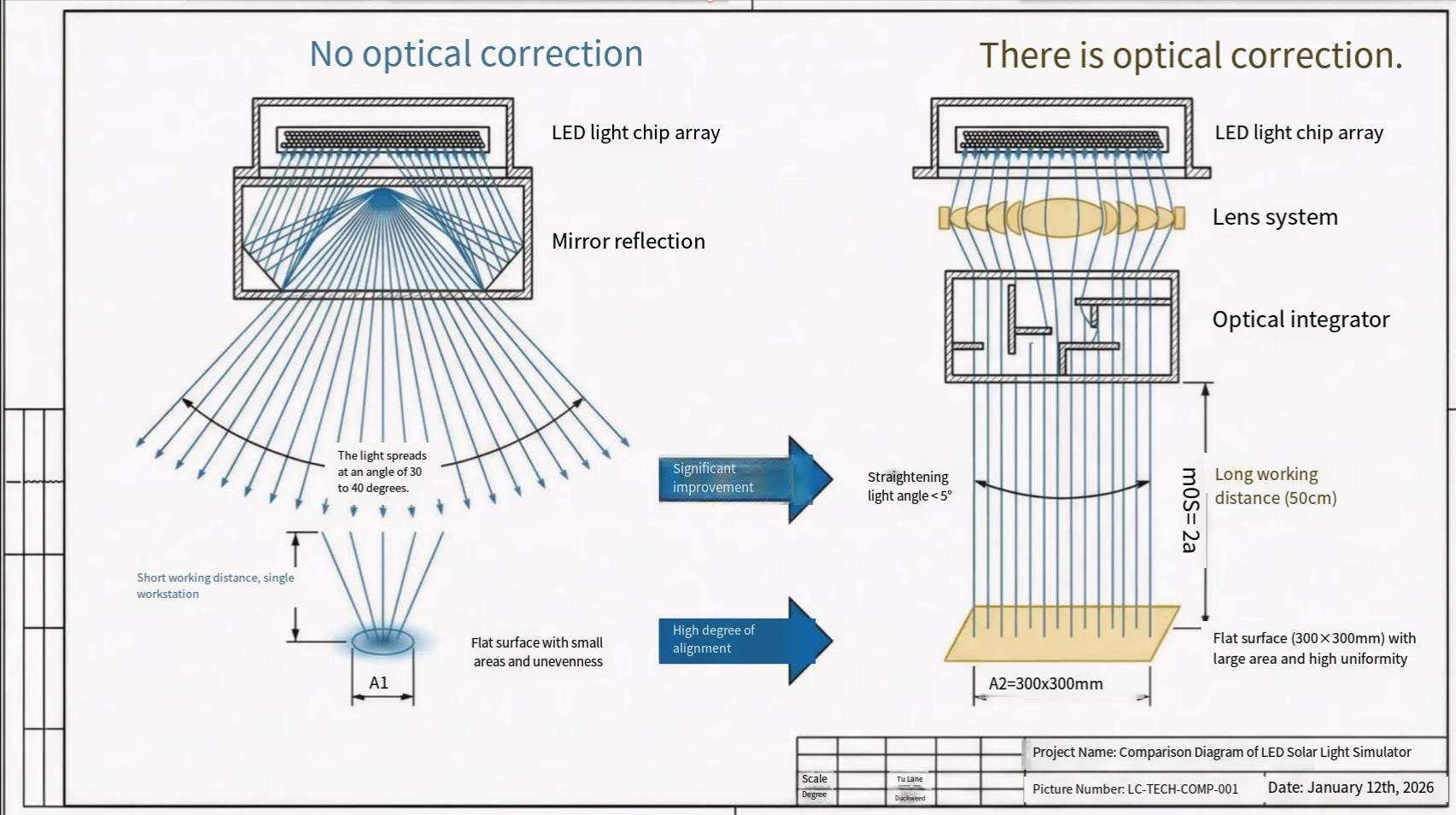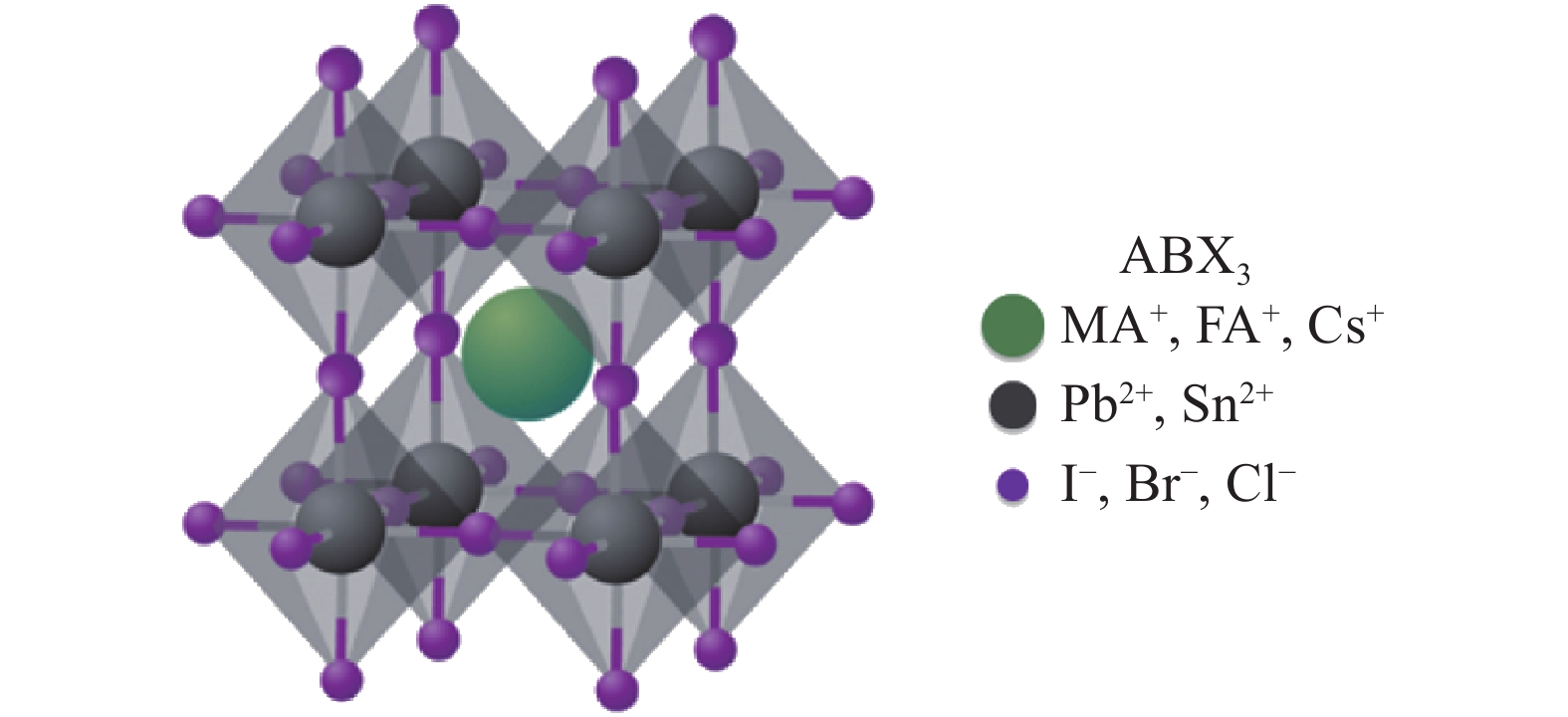
Compared with mature crystalline silicon photovoltaic production lines, establishing a perovskite production line is significantly more complex and challenging. While crystalline silicon module manufacturing relies primarily on physical processes, perovskite production involves intricate chemical formulations and highly customized equipment, posing unique hurdles for industrialization.
1. Fundamental Differences in Production Processes
Crystalline Silicon Production:
The manufacturing of crystalline silicon modules is dominated by physical methods. The process begins with high-purity polysilicon, which is transformed into silicon rods via crystal pulling furnaces. This is followed by a series of steps including cutting, texturing, film deposition, laser etching, and ion implantation. Technologies like TOPCon and BC (back-contact) batteries have further refined specific aspects such as film deposition and laser etching processes. This approach benefits from decades of optimization and standardization.
Perovskite Production:
In contrast, perovskite production hinges on chemical配方 (formulations). Although perovskite has a fixed molecular structure (ABX₃), the variety of materials that can constitute this structure is vast, with hundreds of derivatives already developed. Each new material often requires tailored equipment and processes, drastically increasing the complexity of production line setup
. For instance, RenShuo Guangneng currently employs a wet method to prepare perovskite film layers, while other functional layers are created through physical vapor deposition or evaporation processes. Industry practices vary widely: some use dry-wet hybrid methods, and others even apply wet methods for all functional layers. This lack of uniformity underscores that perovskite processes are not yet standardized.
2. Core Challenges: Materials and Equipment
Equipment Customization and Integration:
Materials and equipment are two central hurdles in the perovskite production line model. Manufacturers offering full-line technical services aim to drive down industry costs by increasing equipment shipments. However, without unified equipment and processes, leading device manufacturers have been relatively slow to launch comprehensive perovskite equipment solutions.
For example, Meyer Burger announced in May plans to raise approximately ¥2 billion to develop a perovskite tandem solar cell equipment industrialization project. Upon completion, the project is expected to produce 20 sets of equipment annually, generating estimated annual revenue of ¥4 billion and a net profit of around ¥600 million.
Currently, perovskite module manufacturers primarily use semi-customized equipment. Traditional crystalline silicon equipment suppliers cannot yet meet all the needs of perovskite production lines. Even those offering full sets of equipment struggle to achieve effective connectivity between different devices. In this customized context, orders from single customers often fail to cover the R&D costs of equipment manufacturers, leading to scenarios where "gross margins are not low but profitability is limited".
Material Challenges:
Material costs remain a prominent issue. As Wang Xuege, Vice President of Ji Dian Guangneng, noted when discussing their "customized full-line delivery" business, the proportion of material costs in the cost per watt of components remains high despite industrialization advances. Communication with upstream and downstream suppliers reveals that the development cycle for perovskite capacity is lengthy for material suppliers. Without the support of large, concentrated orders, cost reduction in materials cannot happen overnight and requires more market participants to invest. The customized full-line delivery model could significantly aid in scaling industry capacity.
3. Lack of Standardization and Process Uniformity
The absence of standardized processes is a critical barrier. Companies like RenShuo Guangneng use wet methods for perovskite layer preparation, while others employ physical vapor deposition or evaporation for other functional layers. Some firms adopt dry-wet hybrid methods, and a few even use wet methods for all functional layers. This diversity highlights the lack of industry-wide process standardization, making it difficult to replicate laboratory efficiencies at scale and integrate equipment from different suppliers seamlessly.
4. Economic and Industrialization Barriers
The high degree of customization required for perovskite production lines means that single customer orders often cannot cover the R&D costs of equipment manufacturers. This results in a paradox where gross margins might appear healthy, but overall profitability is constrained. Additionally, material costs contribute significantly to the overall cost per watt, and reducing these costs requires sustained efforts and broader market participation.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
Building perovskite production lines is fraught with challenges rooted in material diversity, equipment customization, and the lack of process standardization. While companies like Meyer Burger are investing heavily to advance equipment solutions, and industry players are exploring customized delivery models to boost capacity, achieving economies of scale and cost reduction will require continued collaboration across the supply chain, increased standardization, and further technological innovation.
The journey toward perovskite industrialization is still in its early stages, but with concerted efforts in addressing these core challenges, perovskite technology holds the potential to revolutionize the solar industry by offering higher efficiencies and lower costs in the future.