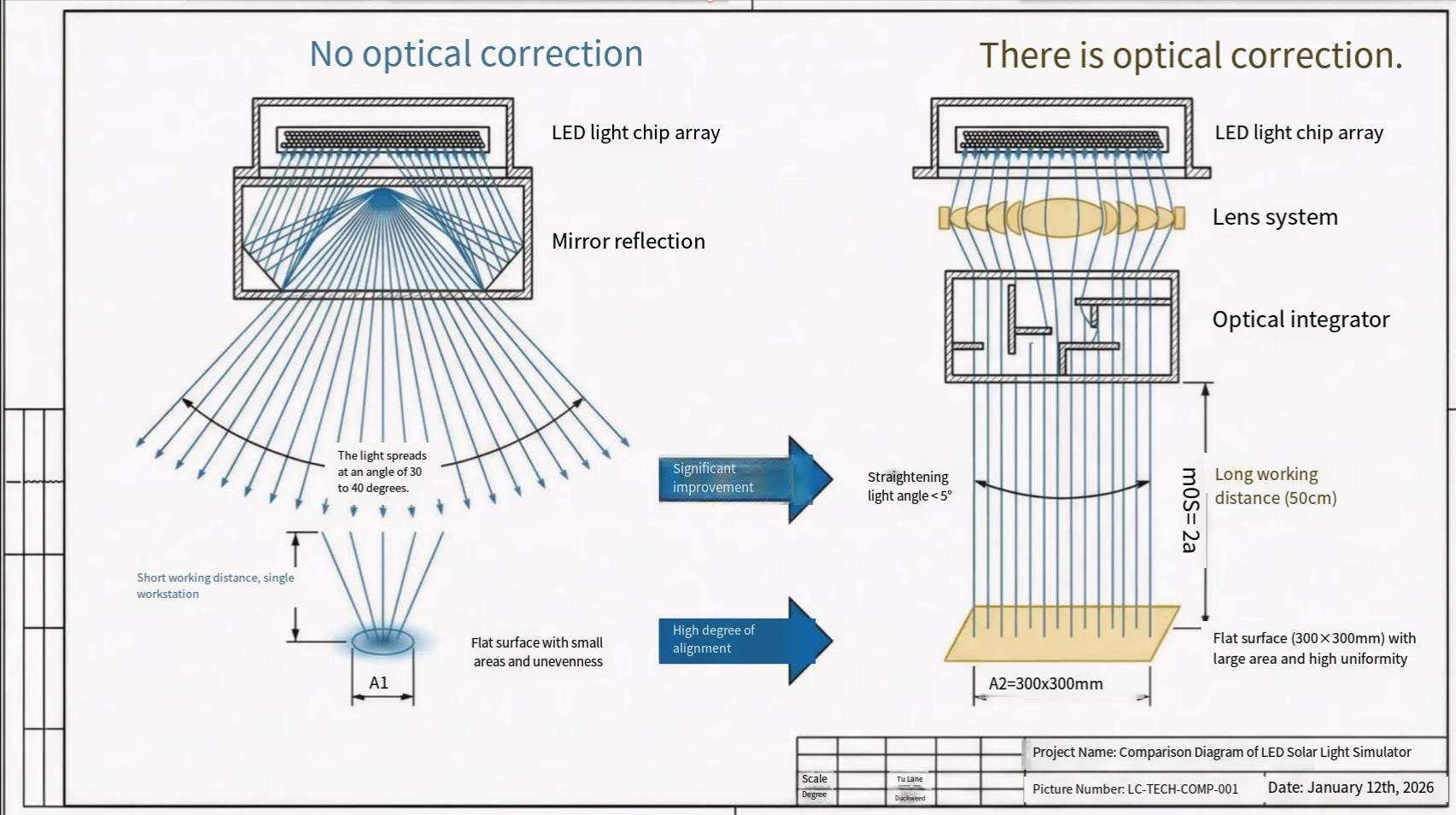
The Global Expansion of the Photovoltaic Industry: Strategies and Future Outlook
The photovoltaic (PV) industry has emerged as a cornerstone of the global transition to renewable energy, driven by technological innovation, policy support, and increasing demand for clean electricity. As countries worldwide strive to meet carbon neutrality goals, the PV industry is undergoing rapid transformation and expansion. This article explores the key trends, regional strategies, and future directions shaping the global layout of the PV industry.
1. Global Market Landscape
The PV industry has experienced unprecedented growth, with global cumulative installed capacity reaching 1,624 GW in 2023 and projected to exceed 4,000 GW by 2030
. China dominates this landscape, accounting for 40% of global installed capacity (656 GW in 2023) and over 70% of solar panel production. Other key players include the European Union (263 GW) and the United States (173 GW), while emerging markets like India, Brazil, and Southeast Asia are rapidly scaling their PV infrastructure. This growth is fueled by declining costs—solar electricity prices have fallen below $0.02/kWh in some regions—making PV energy competitive with fossil fuels.2. Regional Strategies and Industrial Policies
China: Manufacturing Dominance and Technological Leadership
China’s PV industry thrives on its complete supply chain, from polysilicon production to module assembly
. Supported by government policies like the "Dual Carbon" goals, China aims to achieve 1,200 GW of installed capacity by 2025. Companies like JinkoSolar and Trina Solar lead global production, while innovations in perovskite tandem cells and bifacial modules further solidify China’s technological edge. However, trade barriers from the EU and U.S. have prompted Chinese firms to expand overseas manufacturing hubs in Southeast Asia and Africa.
European Union: Quality and Sustainability Focus
The EU prioritizes high-efficiency, environmentally sustainable PV technologies
. Despite relying on imports for over 90% of its solar panels (mostly from China), the EU’s "Net Zero Industry Act" aims to ensure that 40% of clean energy technology is domestically produced by 2030. Initiatives like the European Solar Energy Strategy (targeting 750 GW by 2030) and investments in BIPV (Building-Integrated Photovoltaics) highlight the region’s commitment to innovation and circular economy practices, including panel recycling.United States: Innovation and Domestic Manufacturing Revival
The U.S. focuses on high-efficiency panels and R&D, with states like California and Texas leading installations
. The Inflation Reduction Act (2022) allocates $369 billion to renewable energy, including tax credits for domestic PV manufacturing. While the U.S. currently depends on imports, policies aim to boost local production of silicon wafers and cells, with projects like First Solar’s thin-film factories expanding capacity.Emerging Markets: Rapid Growth and Localization Efforts
Countries like Brazil and India are leveraging abundant sunlight to accelerate PV deployment. Brazil, with 39 GW of installed capacity in 2023, plans to increase solar’s share in its energy mix to 19% by 2050
. However, these regions face challenges in building local supply chains. For example, Brazil still imports 99% of its modules from China. To reduce dependence, governments are imposing tariffs and incentives for local manufacturing, as seen in India’s production-linked incentive (PLI) schemes.3. Technological Drivers of Global Expansion
Next-Generation Solar Cells
Technologies like perovskite tandem cells (with lab efficiencies exceeding 33%) and bifacial modules are redefining performance standards. These innovations enable higher energy yields per square meter, reducing land use and costs.
Energy Storage and Smart Grid Integration
The integration of battery storage systems with PV installations is critical for addressing intermittency
. Lithium-ion batteries dominate, but emerging solutions like flow batteries and solid-state storage are gaining traction. Digital technologies like AI-driven monitoring and blockchain-based energy trading further enhance grid stability and enable decentralized energy systems.Floating Solar and BIPV
Floating PV systems (e.g., deployed on reservoirs) and BIPV (solar-integrated building materials) are expanding PV applications in land-constrained areas
. China and Japan lead in floating solar, while the EU and U.S. adopt BIPV for urban sustainability.4. Challenges and Opportunities
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
Dependence on Chinese manufacturing poses risks, as trade policies (e.g., U.S. anti-dumping tariffs) disrupt supply
. Geopolitical tensions and raw material shortages (e.g., polysilicon) highlight the need for diversified supply chains.Circular Economy and Recycling
With millions of panels reaching end-of-life by 2030, recycling initiatives are essential. The EU leads with extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, while China and the U.S. are developing specialized recycling facilities to recover valuable materials like silver and silicon.
Policy and Investment Barriers
Inconsistent policies and funding gaps in emerging markets hinder growth. However, mechanisms like green bonds and corporate PPAs (Power Purchase Agreements) are mobilizing private investment for utility-scale projects.
5. Future Outlook: Toward a Globalized PV Ecosystem
The PV industry is evolving into a collaborative, globally integrated ecosystem. Key trends include:
Localized Production: Companies like GCL and LONGi are establishing factories in Southeast Asia, Europe, and the U.S. to bypass trade barriers.
Digitalization and AI: AI-powered design tools and predictive maintenance will optimize energy output and reduce costs.
Solar Diplomacy: Developed nations are exporting PV technology to emerging economies, fostering energy access and climate resilience.
By 2030, solar energy is projected to become the world’s primary electricity source, driven by relentless innovation, supportive policies, and cross-border partnerships.
Conclusion
The global expansion of the photovoltaic industry is reshaping energy systems worldwide. While challenges remain, the convergence of technological breakthroughs, strategic policies, and international collaboration will ensure that solar power plays a pivotal role in achieving a sustainable, carbon-neutral future.